Project Files: Download
In this post let’s see how we can Restart Explorer Programmatically with C# in our project.
The inspiration of this blog post is an application I’ve worked on recently. To be more precise it was the installer. When building the MSI installer I needed to create a procedure that will inject a Windows Explorer namespace extension.
But not only that, it needed to unregister the namespace extension, swap/update the files of the application and extension and then register it again. This way the user can start working with it right away.
So how do you keep Windows Explorer off enough time to install and execute your code?
Introducing the Restart Manager
The Restart Manager API can eliminate or reduce the number of system restarts that are required to complete an installation or update.
That was exactly what I needed…
Because Windows Explorer is running during my MSI installer, I was unable to just swap the files. They were in use.
And even if I was able to swap the files, without restarting the explorer the namespace extension was unusable.
Restart Explorer Programmatically App Demo
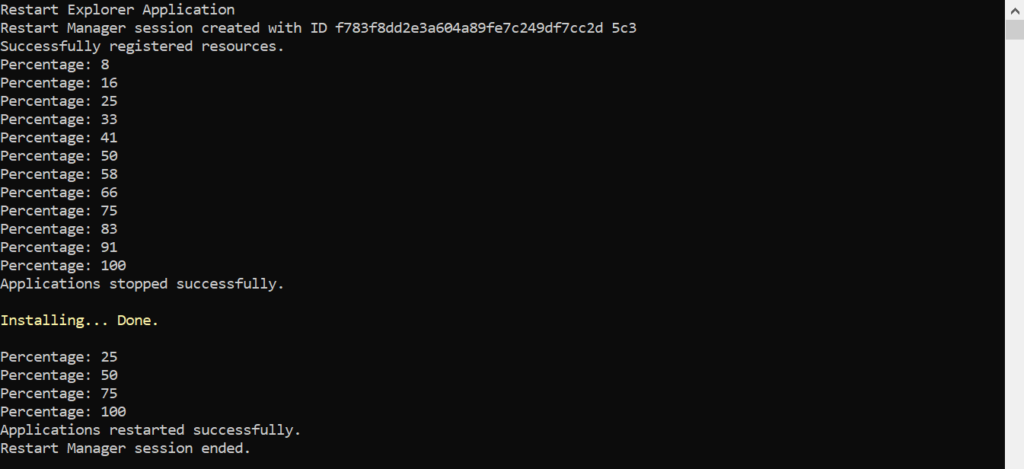
This is the demo application I wrote to accompany this blog post. We will look under the hood in just a sec. Right now you can see that my app has subscribed to two events. One is ReportProgress and the other is ReportPercentage. Once the Windows Explorer application is stopped successfully I can safely install whatever I want.
RestartExplorer class
Lets see how we can use the RestartExplorer class.
RestartExplorer restartExplorer = new RestartExplorer();
restartExplorer.ReportProgress += Console.WriteLine;
restartExplorer.ReportPercentage += (percentage) =>
Console.WriteLine($"Percentage: {percentage}");
restartExplorer.Execute(() =>
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.Write("Installing... ");
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Done.\n");
Console.ResetColor();
});First you need to create an instance of the class. Optionally you can subscribe to the ReportProgress and ReportPercentage events to follow the work of the class.
The main focus is on the method Execute. It allows you to execute your code while Windows Explorer is down.
There are two overloads of the Execute method:
void Execute();
void Execute(Action action);Final Thoughts
So why go thorough all this trouble just to restart Windows Explorer? Well killing explorer is a bit of a rough process. I can only suggest to use the Restart Manager API. The benefit is Explorer knows how to restart itself, and it will restore all opened windows after the restart.
Although, we only talked about Windows Explorer, the same logic goes for all other applications.
