This tutorial will show you how to detect File Content Change using C#.
Sometimes you need to figure out if the content of a file is different. Then, maybe raise an event. But, how do you figure out if there is a file content change, without doing any bit-by-bit file comparisons?
Maybe you can use the LastWriteTime property. Or even the FileSystemWatcher class to detect a user action that might have changed the file. But how about its content? How do we know if the user simply hits Save without doing any changes to the file? Let’s look at a familiar scenario.
Lets say you are working on a Word document. You start typing- then hit save. Consequently, the Modified attribute of the file will be updated. Now, let’s say that you don’t make any further changes to the document. But, you still press the save button.
In both cases the LastWriteTime property will be updated and FileSystemWatcher class will raise a file modified event. But it doesn’t tell us if the file content is changed. When the user saves the file, the native application will go ahead and flush everything from the memory onto the disk. As a result, the system gets a notification that a file is modified. But that’s about it. Now, it is up to us to detect if there is a change in the file content itself.
In this tutorial we will see how to solve this problem. We will discuss how to detect file content change using C#.
Introducing the Hash Algorithm
A Hash Function is a mathematical algorithm, that maps data of an arbitrary size to a bit array of a fixed size. We usually use hashing algorithms to authenticate data. The hash basically works a bit like a seal of approval.
For example, when you download a file off the internet, we can use hash-based verification to ensure that the file is not corrupt. So why we would use hash?
Well, for starters we would like to avoid comparing two files bit-by-bit. Because, it requires two copies of the same file. So, a more popular approach is to generate a hash of the copied file and comparing that to the hash of the original file.
In this case we are doing File Verification. It is the process of using an algorithm to verify the integrity of a computer file, usually by a checksum.
What is a checksum?
A checksum is nothing more than a block of data. You can think of it as a label. A checksum is a string of numbers and letters derived from another block of digital data. All for the purpose of detecting errors.
So, if you want to verify that a copy of a file is identical to the original, you need to use a checksum. The most popular example that I can give you, is the process of file downloading. Once, the download is complete, you can verify the downloaded file integrity by comparing its checksum to the checksum of the original file.
Let’s see a simple C# example:
First, we can set up a string variable like so:
var inputString = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.";If we want to hash this sentence we need to write the following C# code:
using (var hashAlgorithm = MD5.Create())
{
var hash = hashAlgorithm.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(inputString));
string checksum = BitConverter.ToString(hash);
Console.WriteLine(checksum);
}This block of code shows how to create a new instance of a famous hashing algorithm called MD5. Because the ComputeHash function accepts bytes, we need to transform the string into a byte array. As a result, the function returns the hash as an array of 16 bytes.
Since, we want to print the checksum we need to convert the byte hash to string using the BitConverter class. Finally, we can print the checksum string on the console. This is the output:
81-8C-6E-60-1A-24-F7-27-50-DA-0F-6C-9B-8E-BE-28C# Code Explanation
In this simple example we showed how to get the checksum for a string. Let’s go over the process once more and explain it even better.
We start by defining a string that we want to hash. Then, we pass the string as a byte array to a hashing algorithm MD5. Hash functions map binary strings of an arbitrary length to small binary strings of a fixed length. So no matter the size of the string, MD5 will always return the hash as an array of 16 bytes.
A cryptographic hash function has the property that it is computationally infeasible to find two distinct inputs that hash to the same value. And this statement is very important to remember. Because, hashes of two sets of data should match only if the corresponding data also matches.
Even though I am using the word hash instead of checksum, it should not confuse you. The hash algorithm actually produces a checksum. Because, like we said, a checksum is just a string of numbers and letters that uniquely identify a digital data block.
Hashing Algorithm Examples
It may be hard to understand what this code does without seeing it in action.
Imagine that we’d like to hash the answer to a security question. We’ve asked, “What is the name of your favorite pet?”. The answer we are given is: “My favorite pet is my dog Max”. The following block of text shows the answer hashed with MD5 and SHA256 algorithms.
MD5 : 3235e648c08ddd07e51ba332aca71342
SHA256 : 5f6592f41d716687a69be2b92ebe8a08c549ecd11561b3a64e9e2ddb17041b9cNow, imagine that we’ve asked the same question to a different person, and her response is, “Bella”. If we transform the answer into MD5 and SHA256 hash alphanumeric string, here is how the answer would look like:
MD5 : e130fc6de9c40799c78e29ed7b77880a
SHA256 : 604a8e5aa2b19d2cb8a6a6d0f434684ee27451ed7210a3d3df884ffbcf973aefNotice that the original messages don’t have the same number of characters. But the algorithms produce hashes of a consistent length each time. This is another important point to remember. No matter the input length, the hash algorithm will produce a fixed length alphanumeric checksum- output.
Popular Hashing Algorithms
There are many different hashing algorithms. We can use any of the following to detect a file content change. The following is a list of some of the most popular methods:
- MD-5 – You can read more about it here
- RIPEMD-160 – More information is available here
- SHA – Read the details here
What are we going to build?
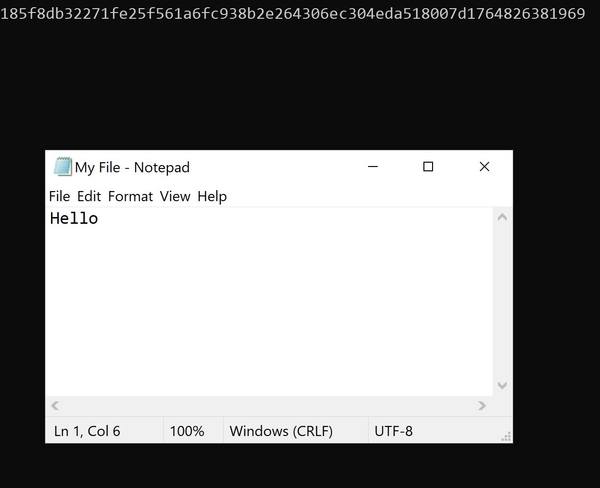
The demo we are about to code in C# is a simple application that should display different checksum when the file content is changed. When I start the application I hash the file: MyFile.txt then I print the checksum on the Console output. You can see the result in the following image
Then I make a small change to the file. I simply add one more sentence to it. And we get the following result:
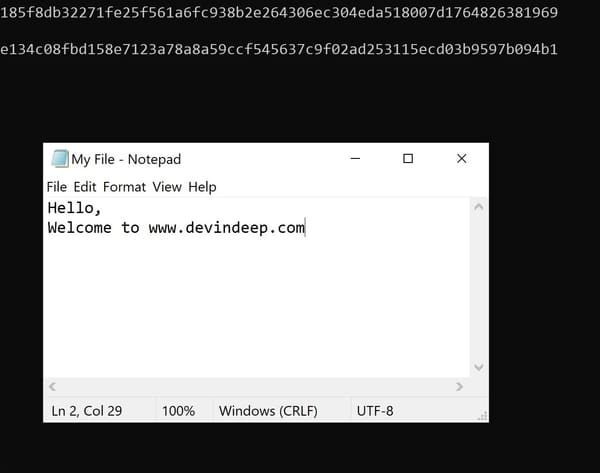
As you can see, right after I change the content of the file the checksum is different as well. This behavior is expected. If I would only hit the save button, without adding more content to the file, then the checksum would be the same.
How to detect a File Content Change?
Well, instead of using the string as an input argument to the hash algorithm, we are going to be using File Streams. It’s as simple as that. Then, instead of comparing the two files byte-by-byte, we can only compare their string checksums.
The procedure is pretty much the same. Except we are going to push a file through the hashing algorithm, which in turn will output a unique alphanumeric string called a checksum, also known as a “hash”.
This will work because the hashing algorithm will always produce a fixed length binary hash. It is always going to be unique in regards to the input file. The hash will be the same, only and only if the two files are 100% identical. As a result, different files, even those with minute differences, produce different checksum values.
So, if there is a real change to the contents of the file, we can verify that by analyzing the checksum.
File Content Change using C#
Now, it’s time to walk through the code.
static void Main(string[] args)=>
ConsoleReader
.ReadUntil(userInput => userInput.ToLower().Equals("q"))
.Do(_ => Console.WriteLine(new FileInfo(AppGlobals.FilePath).ComputeHash(SHA256.Create())));As you can see this is a C# Console Application project. You can start and test this solution like I do, or you can create your own. Because I am working with Console Application project, I will need one special class to gather the user input. So, we are going to create a C# ConsoleReader class.
public class ConsoleReader : IEnumerable<string>
{
private Func<string, bool> predicate = (_) => false;
private ConsoleReader() { }
private ConsoleReader(Func<string, bool> predicate) => this.predicate = predicate;
public static ConsoleReader Create() => new ConsoleReader();
public static ConsoleReader ReadUntil(Func<string, bool> predicate) => new ConsoleReader(predicate);
public IEnumerator<string> GetEnumerator()
{
while(true)
{
var userInput = Console.ReadLine();
if (predicate(userInput)) break;
yield return userInput;
}
}
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() => this.GetEnumerator();
}This class allows the client code to create two types of instances. The first one being, a version where the class can yield every single user input until the user closes the app. And the second version, will end when the user enters a predefined exit character.
Since, we don’t want an indefinite loop I will opt out and create a C# instance of the class with a breaking predicate. A predicate is a simple delegate type that checks if the passed parameter meets some criteria. And, it always returns a bool value.
The logic I want to create for this simple C# file content change app, is to retrieve all user input until the user enters the letter “q“. Which, in turn will stop the application execution.
Now it’s time to add another class. This will be a C# class to extend the behavior of the Enumerable type.
C# Extension Classes
public static class EnumerableExtensions
{
public static void Do<T>(this IEnumerable<T> enumerable, Action<T> onItem)
{
foreach (var item in enumerable)
onItem(item);
}
}I like having this extension method because it allows me to process the user input as it is returned from the ConsoleReader class. Please note that you can use this method with any type that implements the IEnumerable interface.
Finally, we are going to be adding a new C# static class that will hold the ComputeHash method. I think the best place to write this function is inside the FileInfo class.
FileInfo provides properties and instance methods for the creation, copying, deletion, moving, and opening of files, and aids in the creation of FileStream objects.
– Microsoft Documentation
Please note that you can not inherit from this class. That is why I am going to add the following extension method.
Detect File Content Change using ComputeHash function
public static string ComputeHash(this FileInfo fileInfo, HashAlgorithm hashAlgorithm)
{
using (var fs = new FileStream(fileInfo.FullName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.ReadWrite))
{
var hash = hashAlgorithm.ComputeHash(fs);
hashAlgorithm.Dispose();
return BitConverter.ToString(hash).Replace("-", string.Empty).ToLowerInvariant();
}
}It fits perfectly with our logic. The only way you are going to be able to retrieve a checksum for a file is if the file exists and it is indeed a real file. The FileInfo class makes sure that whenever you instantiate an object, it will be of a valid file path.
However, I do want to be able to switch easily between hashing algorithms implemented into the .NET framework. HashAlgorithm represents the base class from which all implementations of cryptographic hash algorithms must derive. But, before using it, please make sure that you have the System.Security.Cryptography namespace included.
The ComputeHash method returns a byte array. But, we want a checksum. We want an alphanumeric representation of the file content. So we need to convert the bytes into a string. To do that, you will need to use the BitConverter class. I would also want to remove the “-” from the string and make it lowercase. Or, feel free to return the string and then process it however you want in your client code. I just prefer it this way.
Since, the HashAlgorithm class implements the IDisposable interface, it’s a good idea to call it.
How File Content Change application works
Well, I wanted to build an application that will inform me when the content of a file is changed. Although this project is simple, you can extend it by attaching an event handler anytime a certain file is modified. But, for the purposes of this tutorial I think this is good enough.
Later on we will see how to implement a solution where it will notify us when a file content is changed. We do have something very similar. You can check How to Detect File Changes with Python. However, we are going to build something very similar with C# as well.
You can also modify this app to receive the file path through the Console. One note before wrapping this tutorial up. To run this C# demo either change the file path inside AppGlobals.FilePath or implement your own logic of retrieving the file path you want to process.
Conclusion
If you work in security, then hashing a critical concept that you have to understand. Hashing is a key way you can ensure important data, including passwords, isn’t stolen by someone with the means to do you harm.
You might also appreciate understanding hashing concepts. There can be numerous reasons why you would need to build a solution very similar to this one. But before you do, make sure you understand the risk factors that each of these cryptographic algorithms brings.
Depending on your particular scenario, you might want to use a different more secure algorithm.
Full Source Code is available at:
DevInDeep/FileContentChange (github.com)
More DevInDeep Tutorials:
How to Create AutoComplete TextBox Control
ML.NET Archives – CODE-AI (devindeep.com)
Neural Networks C# Course Archives – CODE-AI (devindeep.com)
