Introduction
Today we will demonstrate how to obtain Active Windows using C# inside a WPF project.
Full Source Code is available at: DevInDeep/Active Windows (github.com)
Introduction
As software engineers, we often think of processes as the main building blocks of Windows applications. But there’s another dimension: Active Windows. These are the visible (and sometimes hidden) windows that users directly interact with when running applications. For example: Command Prompt, Browser, Notepad, Word etc.
Imagine following a long executing process inside the command prompt. And there is no way to know how far the process is, except inspecting it visually. Or maybe, something has happened inside one of the open applications, and you want to be notified. Sometimes getting this information can be difficult. Not a lot of windows applications return their internal state. But, what if we can change that? What if we can inspect and follow changes from these applications?
If you’ve ever built automation tools, debugging utilities, or productivity apps, you’ve probably needed to get Active Windows or enumerate all running application windows. This requires diving into the Win32 API and learning how Windows OS manages windows at a system level.
In this guide, I’ll share an in-depth tutorial on how developers can retrieve Active Windows using C# and P/Invoke.
Why Getting Active Windows Matters
Windows is a multitasking operating system where users juggle dozens of apps. Developers often need to:
- Track running applications and their Active Windows
- Automate workflows by finding specific Active Windows
- Build productivity tools like custom Alt+Tab switchers
- Create monitoring or security apps that detect suspicious Active Windows
When I built a QA automation tool, one challenge was identifying which Active Window belonged to the SAP GUI. Without mastering APIs like EnumWindows and GetForegroundWindow, that task would have been impossible.
This time we are going to build a simple application that will list the Active Windows. But, this is just a part of a tutorial series. The next chapter will reveal what our goal is, but it will be very similar to the scenario I already touched upon before.
Before moving on with this article, it might be a good idea to learn how to extract text from image. Like I said, not all windows application will expose their internal state. Sometimes, we need a visual inspection of the region that interests us. So, it’s good to know about OCR.
I know this sounds kind of vague, but everything will be revealed in the next tutorial. Right now, just follow along with me so that you can list all Active Windows. Let’s see how we can achieve that.
Core Windows API Functions for Active Windows
To work with Active Windows, you’ll mainly interact with user32.dll through P/Invoke.
What is “User32.dll”?
User32.dll is a core component of the Windows operating system. It provides essential functions for managing the user interface (UI) of Windows applications. Key functionalities include:
- Window Management: Creating, moving, resizing, and destroying windows.
- Input Handling: Processing keyboard and mouse events.
- Message Handling: Managing the message loop for window-based applications.
- Graphics Rendering: Interacting with GDI32.dll to draw graphics and text.
- Clipboard Operations: Functions for copying and pasting data.
What is P/Invoke?
Platform Invocation Services, commonly known as P/Invoke, is a feature in .NET that allows managed code to call unmanaged functions from native libraries, such as those in User32.dll. This is crucial for integrating Windows API functions into .NET applications.
Key Aspects of P/Invoke:
- Function Declaration: You declare the external function in C# using the DllImport attribute, specifying the DLL and the function signature.
- Data Types: P/Invoke requires careful handling of data types, as managed and unmanaged types differ. Attributes can be used to control how data is marshaled between the two.
P/Invoke is often used to access system-level functions, such as displaying message boxes or handling file operations.
How to list Active Windows using C#?
In order to list all the active windows we will need to import the following methods from User32 library:
1. EnumWindows – Enumerate All Active Windows
Enumerates all top-level Active Windows on the desktop.
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
private static extern bool EnumWindows(EnumWindowsProc lpEnumFunc, IntPtr lParam);
private delegate bool EnumWindowsProc(IntPtr hWnd, IntPtr lParam);Usage:
EnumWindows((hWnd, lParam) =>
{
string title = GetWindowTitle(hWnd);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(title))
Console.WriteLine($"Active Window: {title}");
return true;
}, IntPtr.Zero);2. GetForegroundWindow – The Current Active Window
Retrieves the Active Window that has user focus. Please note, we already wrote a tutorial about this.
3. GetWindowText – Fetch the Title of Active Windows
Every meaningful Active Window has a title. But, not all windows provide us with title. So, we need to combine two function imports:
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
private static extern int GetWindowTextLength(HWND hWnd);
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
private static extern int GetWindowText(HWND hWnd, StringBuilder lpString, int nMaxCount);Usage example:
public static string GetWindowTitle(IntPtr hWnd)
{
int length = GetWindowTextLength(hWnd);
if (length == 0) return string.Empty;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(length + 1);
GetWindowText(hWnd, sb, sb.Capacity);
return sb.ToString();
}As you can see, we are simply filtering out windows with no title.
IsWindowVisible – Filter Hidden Windows
Not all Active Windows are visible. Use this function to skip invisible ones.
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
public static extern bool IsWindowVisible(HWND hWnd);GetWindowThreadProcessId – Map Active Window to Process
Every Active Window belongs to a process. This function retrieves it.
GetWindowRect – Get Window Dimensions
Retrieves the dimensions of the bounding rectangle of the specified window. The dimensions are given in screen coordinates that are relative to the upper-left corner of the screen.
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern bool GetWindowRect(IntPtr hwnd, ref Rect rectangle);GetClassName
The GetClassName function retrieves the name of the class to which the specified window belongs.
[DllImport("user32.dll", SetLastError = true, CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
private static extern int GetClassName(IntPtr hWnd, StringBuilder lpClassName, int nMaxCount);GetShellWindow
Retrieves a handle to the Shell’s desktop window.
private static extern IntPtr GetShellWindow();Here is the complete code for method import from User32 library:
public static bool GetProcess(IntPtr hWnd, out Process process)
{
process = null;
try
{
int processID = 0;
GetWindowThreadProcessId(hWnd, out processID);
process = Process.GetProcessById(processID);
return true;
}
catch { return false; }
}
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
private static extern IntPtr GetShellWindow();
private delegate bool EnumWindowsProc(HWND hWnd, int lParam);
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
private static extern bool EnumWindows(EnumWindowsProc enumFunc, int lParam);
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
public static extern bool IsWindowVisible(HWND hWnd);
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
private static extern int GetWindowTextLength(HWND hWnd);
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern bool GetWindowRect(IntPtr hwnd, ref Rect rectangle);
[DllImport("USER32.DLL")]
private static extern int GetWindowText(HWND hWnd, StringBuilder lpString, int nMaxCount);
[DllImport("user32.dll", SetLastError = true, CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
private static extern int GetClassName(IntPtr hWnd, StringBuilder lpClassName, int nMaxCount);
[DllImport("user32")]
private static extern int GetWindowThreadProcessId(IntPtr hWnd, out int processId);Before we implement the main function GetOpenWindows we need only one more data type: WindowInformation.
public class WindowInformation
{
public string Caption { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public string ClassName { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public Process Process { get; set; } = null;
public Rect WindowRect { get; set; }
public bool IsWindowsUI => ClassName.Contains("Windows.UI");
public bool IsOsWindow => Process.ProcessIsStartedFromWindowsDirectory() || IsWindowsUI;
}Now we are ready to enumerate all Active Windows with the following implementation:
public static WindowInformation[] GetOpenWindows()
{
HWND shellWindow = GetShellWindow();
List<WindowInformation> windowInformationList = new List<WindowInformation>();
EnumWindows(delegate (HWND hWnd, int lParam)
{
if (hWnd == shellWindow) return true;
if (!IsWindowVisible(hWnd)) return true;
int length = GetWindowTextLength(hWnd);
if (length == 0) return true;
Rect currentWindowRect = new Rect();
GetWindowRect(hWnd, ref currentWindowRect);
StringBuilder captionBuilder = new StringBuilder(length);
GetWindowText(hWnd, captionBuilder, length + 1);
StringBuilder classNameBuilder = new StringBuilder(1024);
GetClassName(hWnd, classNameBuilder, classNameBuilder.Capacity);
if (GetProcess(hWnd, out Process process))
{
WindowInformation windowInformation = new WindowInformation()
{
Caption = captionBuilder.ToString(),
ClassName = classNameBuilder.ToString(),
WindowRect = currentWindowRect,
Process = process
};
windowInformationList.Add(windowInformation);
}
return true;
}, 0);
return windowInformationList.ToArray();
}GetOpenWindows code walkthrough and reasoning behind it
Let’s now put our knowledge to the test and see how we can get all active windows.
First we get a pointer to the shell window. This is a pointer to our desktop window. Next, we enumerate all the windows that are currently active. For each window we get a pointer.
First we check to see if the pointer belongs to the desktop. If it does, then move on, we are not looking for that window. Next, we check if the window is actually visible on screen. If it is not, then we don’t need it.
The step that follows retrieves the length of the window text and it dismisses that window if the length is equal to zero. The active windows we are after, all have the window text property set.
Next we retrieve the window text, the class name and its position on the screen. Because the enumeration function provides us with a pointer handle of the current active window, we can easily get the process ID. With this information we have extracted we construct a WindowInformation data type and add it to the active windows list.
At the end, we simply return the list as an array.
More Tutorials on DevInDeep:
- How to create Toggle Button in WPF
- How to implement Undo Feature in C# and WPF
- How to create Round Button Control in Win Forms
The Application We Are Going To Build
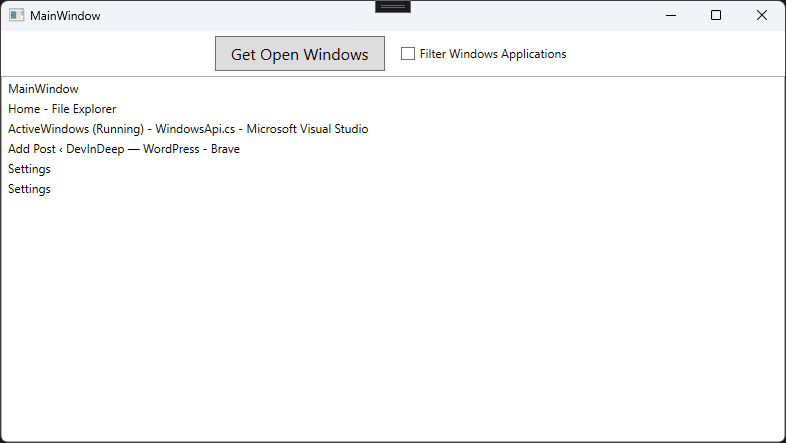
The demo application is pretty simple. We are going to display all active windows inside a list box, upon clicking on the “Get Open Windows” button. There is also a check box that allows the user to filter out Windows OS windows. For example, if you are on Windows 11 and run this application with an administrator account, you will get two additional list items: Settings. This is an OS Window that runs in the background and we can filter it out by checking the “Filter Windows Applications” option.
Main Window XAML Code
<Window
x:Class="ActiveWindows.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:ActiveWindows"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
Title="MainWindow"
Width="800"
Height="450"
Loaded="WindowLoaded"
mc:Ignorable="d">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel
Grid.Row="0"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
Orientation="Horizontal">
<Button
Width="170"
Height="35"
Margin="5"
Click="DisplayOpenWindows"
Content="Get Open Windows"
FontFamily="Segoe UI"
FontSize="16" />
<CheckBox
x:Name="chkFilter"
Margin="10"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
Checked="UseWindowsFilter"
Content="Filter Windows Applications"
Unchecked="UseNoFilter" />
</StackPanel>
<ListBox x:Name="lstOpenWindows" Grid.Row="1" />
</Grid>
</Window>
Main Window C# Code
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
private Func<WindowInformation[]> filter;
public MainWindow() => InitializeComponent();
private void WindowLoaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) => UseNoFilter(sender, e);
private void DisplayOpenWindows(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) =>
lstOpenWindows.ClearWindows().AddWindows(filter());
private void UseWindowsFilter(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) =>
filter = () => WindowsApi.GetOpenWindows().Where(IsNotOsWindow).ToArray();
private bool IsNotOsWindow(WindowInformation windowInformation) => !windowInformation.IsOsWindow;
private void UseNoFilter(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) =>
filter = () => WindowsApi.GetOpenWindows();
}As you can see, there is not much going on here. We have a Func<WindowInformation[]> representing the filtering. When checked if will filter out the WindowInformation array depending on if the window is marked as OS Window.
If you are following with this tutorial, then you will need to implement extension methods for ListBox control and Process class like so:
internal static class ListBoxExtensions
{
internal static ListBox ClearWindows(this ListBox listBox)
{
listBox.ItemsSource = null;
return listBox;
}
internal static void AddWindows(this ListBox listBox, params WindowInformation[] windowInfos)
{
listBox.ItemsSource = windowInfos;
listBox.DisplayMemberPath = "Caption";
}
}internal static class ProcessExtensions
{
internal static bool ProcessIsStartedFromWindowsDirectory(this Process process) =>
process.MainModule.FileName.Contains("WINDOWS");
}It is important to keep in mind that everything we implemented using P/Invoke is placed in the WindowsApi static class.
Real-World Use Cases of Active Windows
There are many examples where this functionality might come handy, and we will see one example being build through this tutorial series. But, for now here are a couple of ideas:
- Application Monitoring Tools – Build custom dashboards to track all Active Windows.
- UI Automation Frameworks – Identify and interact with Active Windows in testing.
- Productivity Apps – Implement custom Alt+Tab features for Active Windows.
- Security Software – Detect hidden or malicious Active Windows.
Common Issues with Active Windows
- Empty titles (not all Active Windows have captions).
- Invalid handles when windows close during enumeration.
- Background UI blocking – enumeration should run in threads.
- Restricted system Active Windows (access denied).
FAQ
How do I get the current Active Window in C#?
Use GetForegroundWindow() to get the handle of the current Active Window, then GetWindowText() for its title.
How can I list all Active Windows in Windows?
Call EnumWindows() and filter with IsWindowVisible() to list all Active Windows.
Can I find which process owns an Active Window?
Yes, use GetWindowThreadProcessId() to map the Active Window to a process.
Why do I see invisible windows in Active Windows enumeration?
Filter them with IsWindowVisible() and by checking GetWindowTextLength().
Conclusion
The ability to retrieve Active Windows is a must-have skill for programmers working on monitoring, automation, or productivity applications. By mastering APIs like EnumWindows, GetForegroundWindow, and GetWindowThreadProcessId, you can build powerful tools that interact with Windows at a low level.
Like I said, this tutorial is part of a series where we will try to extract an internal state of a program that is currently running. So far, we have seen how to use Tesseract library to extract text from image, and now we are listing the all open windows. We already know how to get the active window, so there is one more tutorial in the series and we are ready to showcase our work.
Whether your goal is to build a window manager, a UI testing framework, or a security monitor, understanding Active Windows will give you the control you need to take your applications to the next level.
